How to Identify What Heating System is in Your Home
If you have identified that you have low water pressure in the home, the next best step is to buy a shower or booster pump which will help to increase the flow of water around your home.
But before you choose a pump, you will need to identify which hot water system (boiler type) you have in your home.
In some cases, the boiler heating type you have installed can restrict you to particular booster and shower pumps, or even stop you from installing a pump altogether.
Fortunately, identifying what home heating system you have installed is not particularly difficult.
There are three main types, these are:
Combi-boiler System
Gravity Fed System
Unvented System
Once you have learned the key differences between each, you will be able to quickly identify which system you have installed.
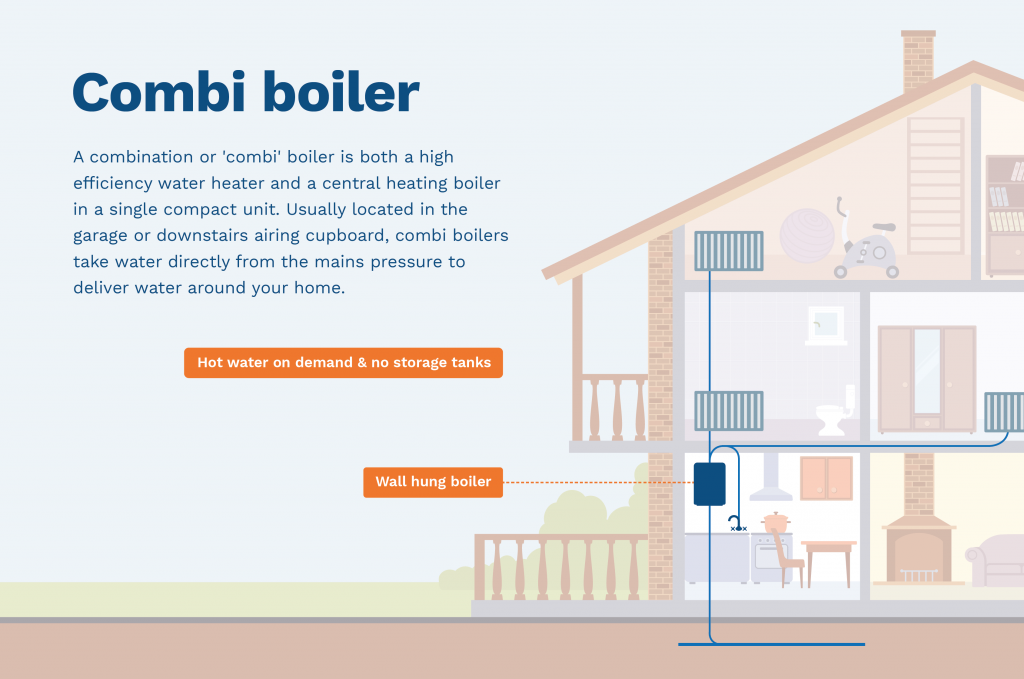
What is a combi-boiler system?
A combination or ‘combi’ boiler is a high-efficiency water heater and a central heating boiler in a single compact unit. Combi-boilers work by taking water directly from the mains water to deliver water around your home.
These boilers do not use water cylinders or storage tanks, so they’re far easier to fit in your home and supply hot water on demand direct from the mains.
Please note that it is illegal to add a shower pump or booster pump directly to a combi-boiler system. This is because the combi-boiler is fed directly from the mains water supply, and you could end up directly affecting the mains water pressure at your neighbour’s home (steal their water). In some cases, you could be liable for any damage to the mains water supply pipes.
Where is a combi-boiler system located?
Combi-boiler systems are usually located in the garage or downstairs airing cupboard. Combi-boilers deliver hot water at the same pressure as the mains, so you typically get a strong, powerful shower without fitting any pumps.
If you are suffering with low water pressure in a combi-boiler system, please contact a combi-boiler certified plumber.
Benefits of a Combi-boiler system
- The compact size of a combi-boiler makes them ideal for smaller properties
- Perfect for when you have limited or no loft space
- Lack of a hot water cylinder increases living space
- Lack of cold water tanks frees up space in the loft (potential loft conversion?)
- No risk of the pipes freezing over winter
- Less pipework in the home makes installation typically cheaper
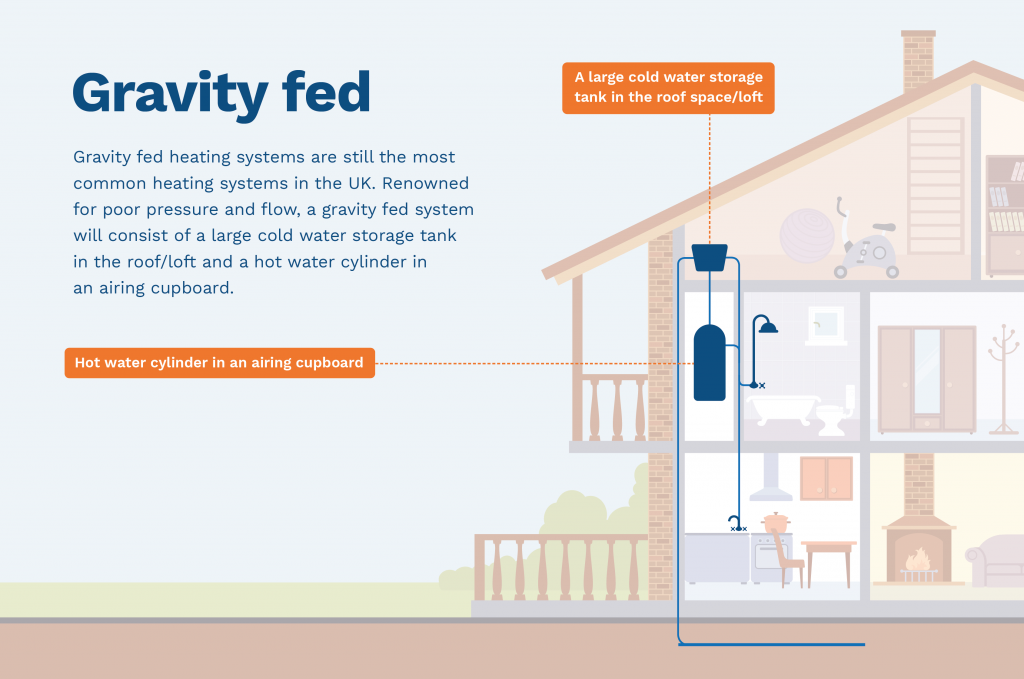
What is a gravity fed system?
Gravity fed systems are the most common hot water heating system used in the UK. Renowned for poor water pressure and flow, a gravity fed system will consist of a large cold water storage tank in the attic and a hot water cylinder located in an airing cupboard near the bathroom.
A gravity fed system can also be known as a conventional boiler, a vent or a regular boiler. There is no difference between these boiler types, simply regional dialect.
One thing to keep in mind is that conventional, gravity fed systems frequently run out of hot water when a shower pump is installed. This is because the shower will now pump more water than your cold water tank was originally designed to hold. Remember, once the supply runs out, it can take a while to replenish.
Also, as the cold water tank is located in the loft, the energy efficiency may be impacted compared to other boilers.
Where is a gravity fed system located?
A gravity fed system will be located in two places. First, the cold water tank will be located in the roof, attic or loft. Second, the hot water cylinder will be located in an airing cupboard, which will usually be located near the bathroom.
This type of central heating system will usually suffer from low water pressure due to lack of pressure in the hot water cylinder.
Benefits of a gravity fed (vented) system
- Ideal for large families where a lot of hot water is used
- Perfect for homes with two or more bathrooms
- A great option for homes where the mains water pressure is quite low
- These systems are compatible with solar water heating systems
Disadvantages of a gravity fed (vented) system
- The need for a cold water tank means a fair amount of space is required to install a gravity fed system
- The need for an immersion heater to produce hot water means the risk of being left with no hot water should the part break down
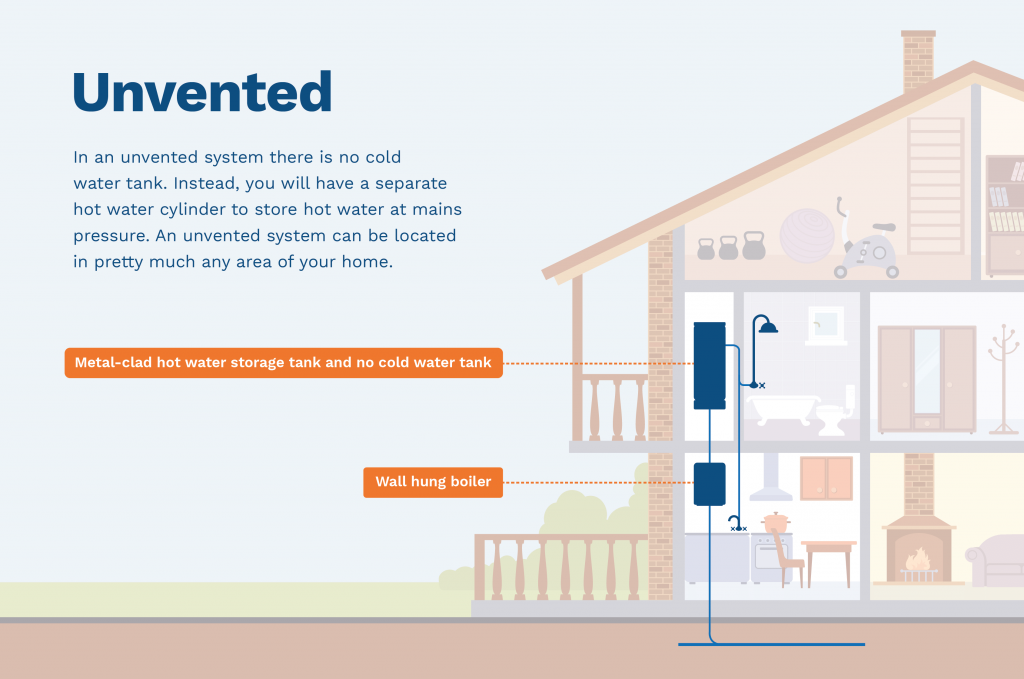
What is an unvented system?
In an unvented system, there is no cold water tank. Instead, you will have a separate, pressurised hot water tank which is fed directly from the cold mains water feed and can, therefore, deliver hot water at mains pressure.
The water can either be heated directly via an immersion heater (an electric heating element that is positioned in the liquid) or indirectly via a central heating system.
Essentially, these boilers are a sort of middle-ground between combi-boilers and conventional boilers. They are also known as sealed systems and system boilers. Again, there is no difference between these boiler types, merely regional dialect.
Where is an unvented system located?
A hot water cylinder will usually be located in an airing cupboard near the main bathroom. You will not have a cold water tank as all water is taken directly from the mains supply.
Benefits of an unvented heating system
- Perfect for a home with more than one bathroom
- Provides hot water to any number of taps at mains pressure
- Lack of a cold water tank frees up space in the loft
- No chance of the pipes freezing over winter
- The economics of running an unvented system is much cheaper
- Built-in components make installation quicker and neater
Disadvantages of an unvented heating system
- If you decide to install an unvented heating system, the hot water flow will now depend on the cold water mains pressure. This means that if the cold water goes off, you will soon lose hot water.